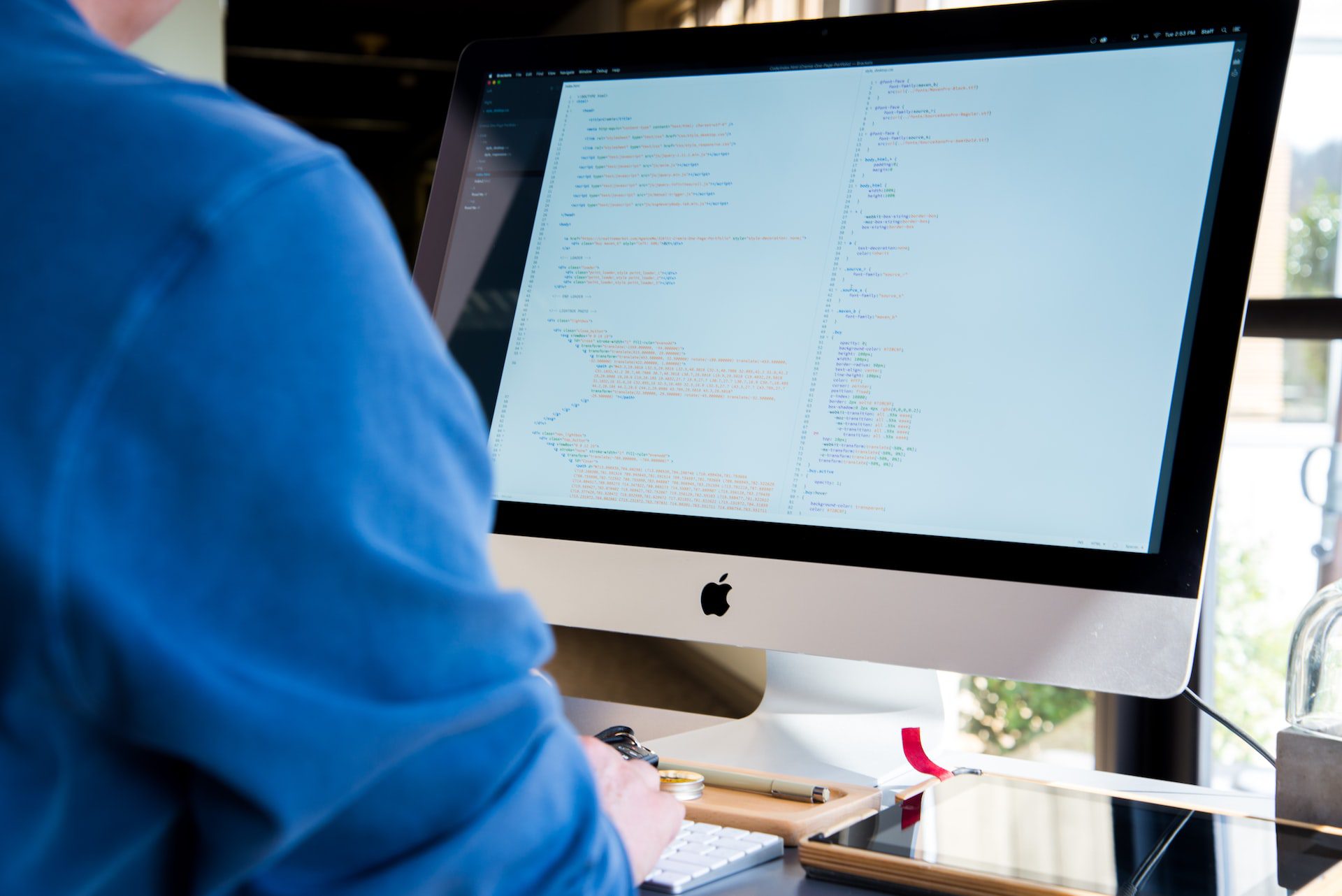
Basically, big data refers to any data sets that are too large or too complex for traditional software to handle. These data sets also often have a large number of fields, which gives them better statistical power.
Structured v unstructured data
Depending on which type of data you are interested in, there are different tools that you can use. For example, structured data has been used for a long time by business users. Unlike unstructured data, structured data is stored in a predefined format. The data can be accessed easily and can be searched. It is also more straightforward to process.
Semi-structured data is another type of big data. It combines elements of both structured and unstructured data. It is a mixture of the two, with its own defining characteristics. For example, it may have semantic tags, organizational properties, and fluidity.
Unstructured data is not stored in a traditional database management system. It is often stored in applications or in a data lake. These types of databases are not designed to analyze and process unstructured data. Therefore, companies handling this type of data will need to hire qualified analysts and engineers to handle the information.
Unstructured data is an enormous quantity of information. It includes text files, videos, audio files, social media content, and satellite imagery. Some of the most common unstructured data is email, open-ended survey responses, call center transcripts, and text messages. These types of data can provide valuable insights to companies. The problem is that the volume of unstructured data is increasing at an accelerated rate. The volume of unstructured data is expected to grow to 35 zettabytes by 2020.
Structured data is stored in a relational database. The data is arranged in a structured manner so that it is easier to process. Typically, structured data is quantitative and consists of hard numbers. The data is stored in fields and can be easily accessed. The data can be analyzed through regression, classification, and clustering.
Usually, unstructured data is stored in native formats. For example, video can be scanned with a tool. It can be extracted to determine the location of an individual or to extract spoken phrases. There are some tools available that can automatically process the data, but these are not very accurate.
Both types of data have the potential to be used in the cloud. However, unstructured data requires more storage space and is more difficult to manage. The tools required to work with this data are more complex and require an understanding of machine learning and data science.
Streaming data
Streaming data is a process of quickly processing and analyzing big data. It is also a method to generate useful trends and insights. This technique brings together the supply and demand of a large network of consumers.
Data streams can be obtained from various sources, including web applications, connected devices, geospatial services, social networks, and ecommerce transactions. These streams are analyzed by different techniques.
Data streaming has become a key part of modern business. It allows organizations to react to changing conditions in real time. This is especially true in the telecom, video, and audio industries. This is because data streams contain real-time information.
It is also possible to use data streams to perform fraud detection. When a transaction is fraudulent, stream processing can stop it before it is completed. In addition, it can be used to detect anomalies in real time.
Another advantage of stream processing is that it has low latency. It also helps to minimize the risk of system failures. The main performance bottleneck is due to lack of memory when working with large amounts of data.
The best companies are positioned to take advantage of data streams. They can leverage the latest technology, products, and information to deliver new insights at scale. They can do this by leveraging both batch and streaming processing techniques.
To make the most of data streams, it is important to design an application that is scalable. It is also necessary to have a competent data presentation that represents a variety of sources. The most important benefit of big data streaming is the real-time intelligence it provides.
The Internet of Things has also fueled the growth of data streams. The data generated from a network of sensors can be integrated with a company’s existing systems. In the case of a ride-sharing app like Lyft, traffic stats, car locations, and pricing are recorded and compared to the rider’s needs. The application then calculates the best driver for the ride and estimates the amount of time it takes to get to the destination.
The paper also presents a systematic review of the state of the art in big data stream analysis. It includes an update on the research landscape, an assessment of the technologies and tools in use, and recommendations for further research.
Varieties of big data
Various varieties of big data are created by human interactions, machine-readable objects, and digital infrastructures. For instance, there are continuous streams of weather, measurements from embedded sensors, clickstreams from websites, and financial markets data.
As a result, big data analytics is important to support decision making. To accomplish this, it is important to have the appropriate processing techniques. It is also necessary to maintain data quality. It is important to recognize the differences in different types of big data and to apply cost-effective techniques. This is particularly true for small businesses, which do not enjoy the same economies of scale as tech giants.
In addition, the value of the big data may not be measured in terms of quantity. For example, a picture or network visualization is a good way to display data analysis results. It is not a complete picture however.
A large data set can also be a distraction. It can also lead to inconsistencies. The key is to determine what is the most important information in a data set and how to resolve it.
The other thing to note is the speed at which the data is generated and stored. Increasingly, business processes generate huge amounts of data. It is important to ensure that the data is consistent and can be retrieved easily. The best solution is to use integrated access to content and data.
Other aspects of the data include velocity, volume, and variety. For example, a census data set is very big in size. It carries a high resolution and has relationality. Despite its size, however, it is not scalable.
There are a few nifty statistical methods that are useful in analyzing this type of data. For example, it is possible to create a map based on edges. It is also possible to display text information in a tree form. There are some technological innovations that can improve the process, including a new technology known as “BigTable”.
The main challenge in handling big data is accelerating the rate of data generation and storage. It is also important to determine the best storage and processing technologies for different purposes.
5 Vs of big data
Using big data to improve your business is a trend that more and more organizations are adopting. But what are the five V’s of big data? These five characteristics of Big Data explain the remarkable potential of Big Data. They also help you understand how to extract value from the data you collect.
The first of the five V’s is volume. Volume describes the amount of data generated, the number of data pieces produced, and the size of the data pieces for analysis. It is a key characteristic of Big Data that relates to the size of the information that can be processed.
The second characteristic is variety. Variety refers to the nature of the data, the types of data, and the distribution of the data. It can also refer to heterogeneous sources. It can be unstructured or structured. It can be from inside or outside the enterprise.
The last characteristic is value. Value refers to what an organization can do with the data it collects and processes. It is the most important of the five V’s of big data, as it relates directly to what an organization can do with the collected data.
Veracity is another important characteristic of the five V’s of big data. Veracity is the level of accuracy of the data. It is important for the organization to get it right. Despite the volume of data, if the data is inaccurate, the organization’s ability to analyze it is compromised.
The final V of the five V’s of big data is value. It is the most elusive. It is the most important for companies to get right. It is the result of comprehensive data integration, analysis, and business decisions. The ultimate quality of the data that an organization has access to determines the impact it has on the company’s business.
The 5 V’s of big data are important because they help businesses to understand how to use big data. By recognizing and addressing these five V’s, companies can begin to harness the power of big data to improve their operations and customer service.
It is important to understand that there are many different ways to structure the data. Incomplete data can cause confusion or life-threatening situations. Getting the data right is the most important part.